Technical SEO is like fixing up your house so that search engines (like Google) can easily find, understand, and like it. It’s about making sure the “house” is built right, so it shows up high in search results when people look for what you offer.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy is it important?
- More visitors: A well-built website is easier for search engines to find, which means more people will see it.
- Better user experience: A fast, easy-to-use website keeps people coming back.
- Higher rankings: Search engines reward websites that are easy to navigate and understand.
So, what does technical SEO actually mean?
- Speed: How quickly does your website load? A slow website is like a house with a creaky front door.
- Mobile-friendliness: Does your website look good on phones? Most people use their phones to search, so this is crucial.
- Structure: Are your pages organized in a way that’s easy to understand? Think of it like a clear floor plan.
- Technical stuff: Things like XML sitemaps, robots.txt, and other technical jargon that help search engines understand your website.
In this post, we’ll explore 7 common technical SEO issues that could be holding your site back from ranking higher—and how to solve them.
1. Duplicate Content Issue Due to HTTP and HTTPS
The problem:
Do you have both an HTTP and HTTPS version of your website? If so, you might be facing duplicate content issues without even realizing it. Search engines can see these as two different websites with the same content, which can confuse them and lead to ranking penalties.
The solution:
Ensure that your website consistently uses only HTTPS. If both versions exist, set up a 301 redirect from the HTTP version to the HTTPS version. This tells search engines that the HTTPS version is the preferred one. Also, update internal links to point only to the HTTPS version.
2. Missing or Incorrect Canonical Tags
The problem:
Canonical tags tell search engines which version of a page to index when there are multiple versions of the same or similar content. Without them, or if they’re incorrectly set, search engines might index the wrong page, or worse, consider both pages as duplicates.
The solution:
Add a rel=“canonical” tag to each of your pages, pointing to the preferred version. This simple tag ensures search engines know which URL is the primary one to rank. If you have pages with slightly different URLs but the same content, make sure the canonical tag points to the original page.
3. Slow Website Speed
The problem:
We live in a fast-paced world, and users don’t have time to wait for slow websites. If your pages take too long to load, not only will users leave quickly (increasing your bounce rate), but search engines will also rank you lower. Google, for example, uses site speed as a ranking factor.
The solution:
Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to test your website’s speed. You can improve speed by optimizing images (using compressed formats like WebP), minifying CSS and JavaScript files, and enabling browser caching. For more significant speed boosts, consider switching to a faster hosting provider or using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to serve your content more quickly.

4. Broken Links (404 Errors)
The problem:
Broken links, also known as 404 errors, occur when a page on your site no longer exists or the URL has changed without a redirect. These links hurt user experience and make your site seem outdated to search engines.
The solution:
Regularly check your site for broken links using tools like Google Search Console or Screaming Frog SEO Spider. Fix these links by either updating them or setting up 301 redirects to point users to the correct or new page. This will improve both user experience and search engine crawling.
5. Non-Optimized Mobile Experience
The problem:
With the rise of mobile browsing, Google has adopted mobile-first indexing, meaning your website’s mobile version is prioritized for indexing and ranking. If your website doesn’t provide a good mobile experience—like if it’s slow, hard to navigate, or not responsive—you could see a drop in your rankings.
The solution:
Ensure your website is mobile-friendly by using a responsive design that adjusts to different screen sizes. Other improvements include optimizing images for mobile, simplifying navigation, and reducing mobile page load times.
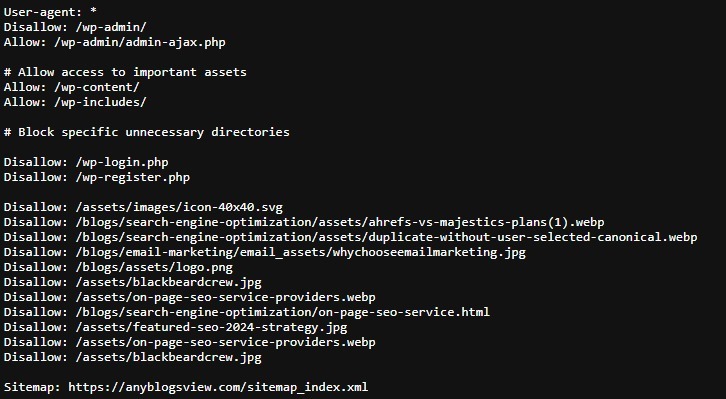
6. Improper Use of Robots.txt
The problem:
Your site’s robots.txt file tells search engines which pages they can and cannot crawl. However, an incorrectly configured robots.txt file can block important pages, such as your homepage or blog posts, from being indexed. This means search engines won’t even see your content to rank it.
The solution:
Check your robots.txt file for any disallow rules that may be preventing critical pages from being crawled. If you want a page indexed, ensure it’s not disallowed in the robots.txt file. You can also use the robots.txt tester in Google Search Console to find and fix any issues.
7. Duplicate Meta Tags
The problem:
Meta titles and descriptions are what users see on the search results page. If multiple pages on your website have the same meta tags, it confuses search engines, making it harder for them to understand the focus of each page. This can dilute the relevance and ranking of your content.
The solution:
Every page on your website should have unique meta titles and descriptions. This makes it easier for search engines to understand what each page is about and match it to relevant queries. Tools like Yoast SEO for WordPress can help you easily update your meta tags, ensuring each page has a unique, keyword-optimized title and description.