Table of Contents
A few months ago, thousands of leaked documents surfaced from Google’s vault, revealing secrets about their search engine algorithm that they never wanted the public to see. These documents brought to light four shocking discoveries that, if true, change everything. For over a decade, Google has denied the existence of these practices, but now, there’s more evidence to question their transparency.
Even though a few experts have called Google out for misleading the public, most of these voices were ignored. After a poll on Twitter, 72% of users believe Google is actively deceiving us. This raises a crucial question: Why would Google lie about its algorithm? What could the company gain by keeping these practices hidden from the millions who rely on their guidelines for website optimization?
Could it be a misunderstanding, or is something more sinister? If Google, a company that once vowed to “not be evil,” is manipulating us, who can we trust?
The Chrome Data Mystery
Our journey began in 2012 and focused on a product many of us use daily: Google Chrome.
At a search engine marketing conference, Matt Cutts, a former Google engineer, was asked if Chrome browser data was used in Google’s search ranking. Cutts denied it.
The rumors about Chrome data being used faded after Cutts left the company, but the leaked documents revealed a different story. They pointed to a module called Chrome In Total, showing that Google was collecting clickstream data—basically a map of everything users do online. This data tracks the websites you visit, the links you click, and even how long you stay on a page.
This information is incredibly valuable for businesses to understand user behavior, but it’s a gold mine for Google. Since Chrome is used by 63% of internet users, Google can see how over half the planet interacts with the web, not just search results.
Why Would Google Hide Chrome Data Usage?
But why lie about using Chrome data? The answer may be tied to Google’s competitive history. In the early days, Google was competing with other search engines like AltaVista and MSN Search. To stay ahead, they might have kept these methods secret. By using Chrome’s data, Google could dominate other sectors like video, maps, and finance.

The motivation is simple: money. As a public company, Google has to make more profits every quarter. Chrome data helps them stay ahead by keeping other competitors out of the market.
The Click Data Controversy
One of the most valuable pieces of data from Chrome is click data. When users search for something and click on a result, Google can track that action. For example, if you search for “running shoes” and click on a comparison guide, Google sees that behavior. If many users do the same, it sends a strong signal to Google about which type of content is most helpful.
Despite this, Google has repeatedly denied using click data in their ranking algorithm.
In 2015, Gary Illyes, a Google analyst, said that using clicks in rankings would be a mistake. However, the leaked documents revealed a system called Navboost, which uses click data to improve search results.
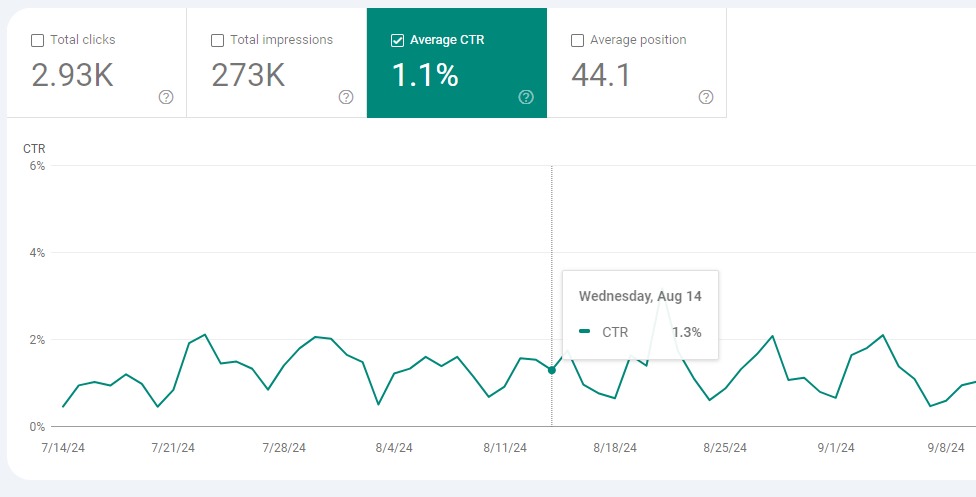
The Truth About Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Click-through rate (CTR) is also a big factor. Although Google says it doesn’t use CTR for search rankings, it provides CTR data in Google Search Console, suggesting it’s important.
The leaked documents confirm that Google does look at various types of clicks to understand user experience better, including:
- Good clicks
- Bad clicks
- Last longest clicks
The likely reason Google denies using clicks is to prevent manipulation. If people knew for sure that clicks affected rankings, click farms and bots would flood the system.
The Site Authority Lie
Another big revelation from the leaked documents is the existence of site authority, a metric Google uses internally to rank websites. Google has publicly denied using something called Domain Authority (DA), a metric widely used in SEO. However, the leaked documents show that Google does have a metric that measures a site’s overall authority.
The Google Sandbox: Is It Real?
This authority metric plays a big role in rankings, especially for new websites. In the past, SEO professionals talked about something called the Google Sandbox, a place where new websites were supposedly placed until Google could trust them. Google has denied the existence of the Sandbox for years, but the documents revealed a similar concept called Host Stage. This feature helps Google filter out fresh or spammy sites before they appear in search results.
Moving Forward with Caution
The leaks suggest that while Google isn’t intentionally lying all the time, they are definitely not telling the whole truth. The information shared by Google’s spokespeople might be designed to mislead spammers, but it also leaves SEO professionals in the dark.
As content creators and webmasters, we need to test and verify everything we hear from Google. It’s better to rely on data, testing, and the broader SEO community rather than taking Google’s word at face value.
In the end, while Google’s search algorithm is highly sophisticated, we can’t afford to blindly trust everything they say. Instead, we should share knowledge, stay informed, and continue testing to understand what really works in SEO.
Google’s search engine may be the best, but the secrets revealed in these leaked documents show that their dominance comes with a cost—one that we’re only just beginning to understand.
Discover the untold potentials of Google with this comprehensive exploration into Google Chrome secrets, Google Home tips, and understanding Google Sandbox in SEO. Uncover hidden functionalities in Google Chrome that enhance your browsing experience while maximizing efficiency and privacy. Master the use of Google Home by learning its secrets to make your everyday tasks easier, from setting up routines, remembering important dates, to controlling smart home devices. Lastly, navigating Google Sandbox in SEO will no longer be perplexing when you know the fundamental role it plays in new websites’ rankings. Understanding its implications can aid in planning a superior SEO strategy for better Google rankings.
Discover a myriad of hidden features with Google Chrome secrets and Google Home secrets that can significantly enhance your user experience. Google Chrome secrets include useful shortcuts and hidden features that simplify browsing, while Google Home secrets help you make the most of your smart speaker with unseen apps and voice commands. Additionally, understanding Google Sandbox SEO is essential for any website owner. It’s a filter that Google uses to prevent new websites from ranking high in search results immediately, ensuring a level playing field in search engine rankings. Knowledge of these areas will empower you to utilize Google products more effectively and optimize your website’s SEO strategy.
Google’s search system involves a myriad of algorithms and factors, some of which remain hidden, to optimize the results you see on your screen. Uncovering the secrets of the Google search engine presents interesting features like advanced search operators that streamline your queries. In the Google search bar, secrets for significant results include using quotation marks for exact phrases, the asterisk as a wildcard, and the minus symbol to exclude specific words. Understanding and employing these methodologies can enhance the precision and effectiveness of your Google search experience.
Google’s search engine operates on a complex algorithm, which sometimes may appear as if it’s hiding search results or suppressing information. However, it’s not about hiding the truth but rather about prioritizing relevant, reliable, and trustworthy content. It uses multiple factors, like keyword relevance, site authority, and user behavior, known as ‘Google Search Engine secrets.’ To get the most out of your Google search, understanding these ‘secrets’ can significantly enhance your search experience. They’re all about using specific commands and keywords systematically to filter and modify your search results more accurately.
Google’s algorithm is designed to deliver the most relevant and trustworthy results, but it can sometimes be misunderstood as “hiding the truth”. Its inner workings remain quite secretive to maintain a fair and balanced search environment. Google uses a variety of factors, like relevance, site quality, and other undisclosed elements, to rank search results. These “secrets” aim to prevent manipulation, ensuring users get the most accurate information. To effectively use Google Search, understanding these factors can help refine your searches for more precise results.